Understanding Intelligent Agents in AI
Estimated reading time: 10 minutes
Key Takeaways
- An intelligent agent in AI is a software program capable of perceiving its environment and making autonomous decisions.
- These agents function by integrating perception, decision-making, and action layers.
- Intelligent agents have varied applications in industries like healthcare, finance, and entertainment and come with ethical and technical challenges.
- The future of intelligent agents is linked to advancements in learning, decision-making, and autonomy.
Table of contents
What is an Intelligent Agent?
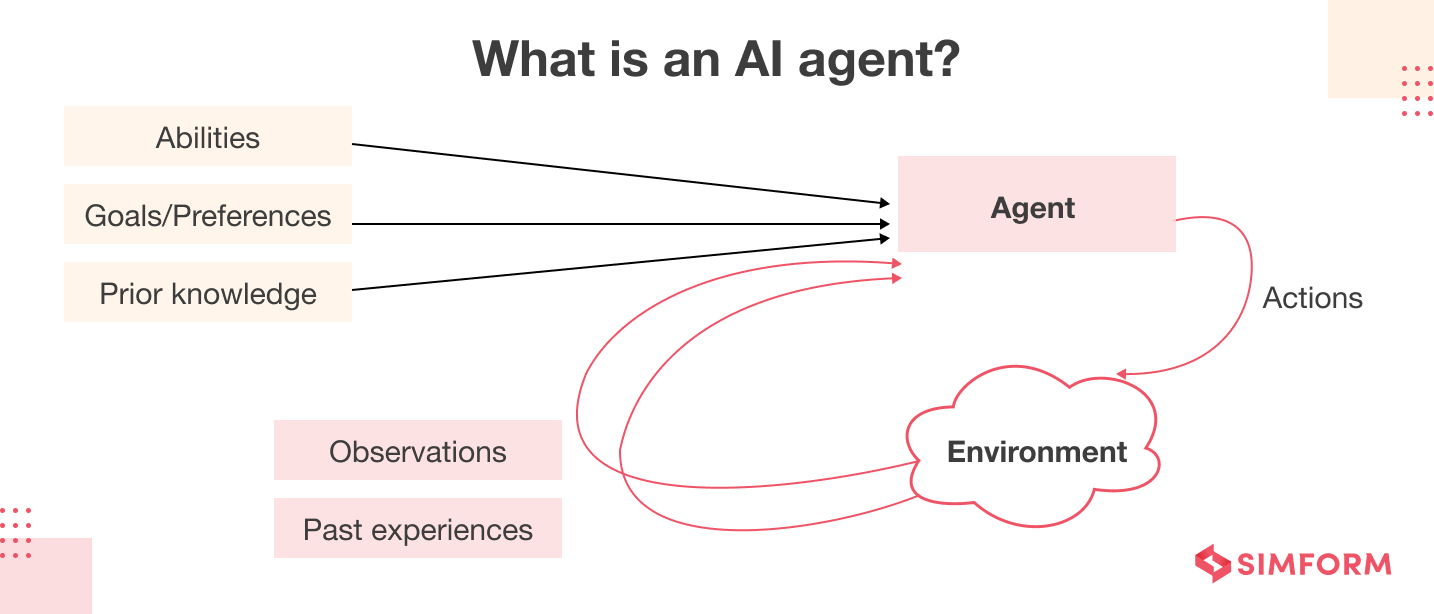
An intelligent agent is a software entity that operates autonomously within its environment. Think of it as a digital “worker” that can:
- Perceive its surroundings through various inputs
- Process information using sophisticated algorithms
- Take actions based on its analysis
- Learn from experience to improve performance
These agents are foundational to modern AI systems, capable of adapting to changes without constant human intervention. Learn more here.
[Source: Understanding AI Agents 101, AWS AI Agents]
How Intelligent Agents Work
The functionality relies on a sophisticated layered architecture:
Perception Layer
- Gathers information through sensors or data inputs
- Processes raw data into usable information
- Maintains awareness of environmental changes
Decision-Making Layer
- Analyzes processed information
- Applies AI algorithms to evaluate options
- Selects optimal actions based on goals
Action Layer
- Executes chosen decisions
- Implements changes through various outputs
- Monitors results for feedback
[Source: Simform AI Agents, Moveworks AI Agents]
Types of Intelligent Agents
Different situations require different types:
Simple Reflex Agents
- React based on current perception
- Use predefined rules
- Best for predictable environments
Model-Based Agents
- Maintain internal state representation
- Track environment changes over time
- Handle partially observable situations
Goal-Based Agents
- Work toward specific objectives
- Plan sequences of actions
- Evaluate multiple possibilities Learn more
Utility-Based Agents
- Maximize performance metrics
- Balance competing objectives
- Optimize for best outcomes
[Source: GeeksforGeeks AI Agents]
Applications of Intelligent Agents in AI
Virtual Assistants
- Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant
- Natural language processing
- Task automation and scheduling
- Personalized responses
[Source: Smythos AI Characteristics, Simform AI Agent]
Autonomous Vehicles
- Environmental sensing
- Route planning
- Real-time decision making
- Safety systems Safety overview
[Source: AWS AI Agents]
Recommendation Systems
- Content suggestions
- Product recommendations
- Personalized experiences
- Learning from user behavior Learn more
[Source: Smythos AI Characteristics]
Industry Impact
Healthcare
- Diagnostic assistance
- Treatment planning
- Patient monitoring
- Administrative automation
Finance
- Trading algorithms
- Fraud detection
- Risk assessment
- Portfolio management
Entertainment
- Gaming AI
- Content curation
- Interactive experiences
- Personalized streaming
[Source: Understanding AI Agents 101, Moveworks AI Agents]
Challenges and Limitations
Ethical Considerations
- Privacy concerns
- Decision transparency
- Bias prevention
- Accountability measures Read more
[Source: Understanding AI Agents 101]
Technical Limitations
- Environmental complexity
- Processing power requirements
- Real-time performance
- Reliability issues
[Source: Smythos AI Characteristics, Simform AI Agent]
The Future of Intelligent Agents in AI
As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see:
- More sophisticated decision-making capabilities
- Better integration with IoT devices
- Enhanced natural language understanding
- Improved multi-agent collaboration
- Greater automation in complex tasks Discover more
[Source: Moveworks AI Agents]
Breakthrough areas include:
- Advanced reinforcement learning
- Emotional intelligence
- Contextual understanding
- Autonomous problem-solving
- Multi-agent systems Explore here
[Source: Understanding AI Agents 101]
Conclusion
Intelligent agents represent a fundamental building block of modern AI systems. Their ability to perceive, decide, and act autonomously is transforming industries and creating new possibilities for automation and innovation. As technology continues to evolve, these agents will become increasingly sophisticated, offering even more powerful solutions for complex challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main components of an intelligent agent?
The main components include the perception layer, decision-making layer, and action layer, enabling agents to perceive the environment, decide on actions, and execute them accordingly.
What types of environments do intelligent agents operate in?
Agents can operate in various environments, including fully observable, partially observable, deterministic, and stochastic environments, depending on the complexity and requirements of their tasks.
What is the role of intelligent agents in AI development?
Intelligent agents are central to AI development, providing autonomous capabilities for tasks such as data analysis, decision-making, and executing actions, across numerous industries.
